Home insurance premiums in Canada can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for securing affordable and adequate coverage. This guide delves into the key elements influencing your home insurance costs, from location and property characteristics to insurance company practices and government regulations. We’ll explore how different insurers price their policies, what discounts are available, and how to navigate the claims process.
Ultimately, this will empower you to make informed decisions about protecting your most valuable asset.
We’ll examine the impact of geographical location, considering high-risk areas prone to natural disasters and those with lower risk profiles. The age and construction materials of your home play a significant role, as do the coverage amounts you choose. We’ll also compare pricing strategies of major insurers, explore available discounts, and Artikel the steps involved in filing a claim effectively.
By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of what affects your premiums and how to get the best value for your money.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Premiums
Several key factors influence the cost of home insurance premiums in Canada. Understanding these factors can help homeowners make informed decisions and potentially save money. These factors interact in complex ways, and the overall premium is a reflection of the insurer’s assessment of risk.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Costs
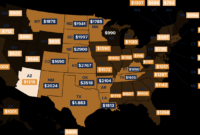
Your home’s location significantly impacts your insurance premiums. Provinces like British Columbia and Ontario, particularly areas prone to wildfires, earthquakes, or flooding, tend to have higher premiums than those in provinces with fewer natural disaster risks. For example, coastal areas of British Columbia facing tsunami risks or areas of Alberta susceptible to hailstorms will generally see higher premiums. Conversely, areas with lower crime rates and fewer claims histories, such as certain smaller towns in the prairies, may enjoy lower premiums.
Specific neighbourhoods within a city also play a role; a home situated in a high-crime area will likely cost more to insure than one in a safer, more affluent neighbourhood.
Home Age and Insurance Premiums
Older homes generally command higher insurance premiums than newer ones. This is because older homes often have outdated plumbing, electrical systems, and building materials that are more susceptible to damage or failure. Furthermore, older homes may not meet current building codes, leading to increased vulnerability to certain types of damage. For instance, a 100-year-old home might require more extensive repairs after a storm compared to a newly built home, resulting in a higher insurance premium for the older property.
While precise figures vary widely based on location and other factors, it’s not uncommon to see a difference of 10-20% or more between the premiums of a comparable older home and a newer one.
Building Materials and Insurance Rates, Home insurance premiums in Canada
The materials used in your home’s construction directly affect your insurance premiums. Homes built with fire-resistant materials like brick or concrete typically have lower premiums than those constructed primarily of wood. Wood-framed homes are more vulnerable to fire damage, leading insurers to assess a higher risk. A brick home, for example, might enjoy a 5-10% lower premium than a comparable wood-framed home in the same location, reflecting the reduced risk of fire damage.
The type of roofing material also plays a role; homes with fire-resistant roofing materials will generally receive more favorable rates.
Coverage Amounts and Premium Costs
The amount of coverage you choose significantly impacts your premium. Higher coverage levels mean higher premiums, as the insurer is assuming a greater financial responsibility in case of damage or loss. The following table illustrates this relationship:
| Coverage Amount | Estimated Premium (Example – Varies by location and other factors) | Estimated Premium (Example – Varies by location and other factors) | Estimated Premium (Example – Varies by location and other factors) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | $1,200 | $1,500 | $1,800 |
| $750,000 | $1,500 | $1,875 | $2,250 |
| $1,000,000 | $1,800 | $2,250 | $2,700 |
Insurance Company Practices and Pricing
Understanding how insurance companies set their prices is crucial for securing the best home insurance rates. Several factors influence their pricing strategies, including risk assessment, competition, and operational costs. This section delves into the practices of major Canadian providers, common discounts, and the process of premium determination.
Pricing Strategies of Major Canadian Home Insurance Providers
The pricing strategies of Canadian home insurance providers are complex and often vary based on location, risk assessment, and individual customer profiles. However, some general observations can be made by comparing the approaches of three major players.
- Company A: This company often employs a competitive pricing strategy, aiming to offer rates that are generally in line with or slightly below market averages. They may focus on attracting a large customer base through broader appeal and potentially less stringent underwriting criteria. This can lead to slightly higher premiums for lower-risk individuals to offset higher-risk customers.
- Company B: This provider frequently uses a more targeted approach, focusing on specific customer segments (e.g., those with high credit scores or specific home features). They may offer highly competitive rates to these segments while charging more to those perceived as higher risk. This strategy allows for a more refined risk management approach.
- Company C: This company might emphasize bundled services and loyalty programs, offering significant discounts to customers who combine home and auto insurance or maintain long-term policies. This strategy aims to build customer retention and loyalty over time.
Common Discounts Offered by Insurance Companies
Many insurance companies offer discounts to incentivize preventative measures and reward responsible behaviour. These discounts can significantly reduce your premiums.
| Discount Type | Description | Potential Premium Reduction | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bundling | Combining home and auto insurance with the same provider. | 5-15% | A customer bundling their home and auto insurance might save $200 annually. |
| Security Systems | Installing and maintaining approved security systems (alarm, monitored systems). | 5-10% | A home security system could lower premiums by $100 per year. |
| Claims-Free History | Maintaining a clean claims history for a specified period. | 5-20% (depending on length of history) | Five years without claims could result in a $300 annual savings. |
| Loyalty/Long-Term Policy | Maintaining a policy with the same insurer for a prolonged period. | 2-5% (per year, up to a certain limit) | A customer with a 10-year policy might receive a 5% discount. |
Insurance Company Risk Assessment and Premium Determination
Insurance companies use a multi-step process to assess risk and calculate premiums. This process is designed to fairly reflect the likelihood of a claim.
- Data Collection: The insurer gathers information about the property, including its location, age, construction materials, and security features. They also collect information about the homeowner, including their credit history and claims history.
- Risk Assessment: Using sophisticated models and algorithms, the insurer analyzes the collected data to assess the likelihood of various types of claims (fire, theft, water damage). Factors like proximity to fire hydrants, crime rates, and the age of the home’s plumbing system play a significant role.
- Premium Calculation: Based on the risk assessment, the insurer calculates a base premium. This base premium is then adjusted based on various factors, including the discounts mentioned earlier.
- Premium Adjustment: The base premium is adjusted based on the individual’s risk profile and any applicable discounts. This results in the final premium offered to the customer.
Impact of Claims History on Future Premiums
Your claims history significantly impacts future premiums. Filing a claim, even a small one, can lead to a premium increase.
- Example 1: A homeowner with a minor claim (e.g., a broken window) might see a 5-10% increase in their premium the following year. This increase reflects the increased perceived risk associated with the property.
- Example 2: A homeowner with multiple claims over a short period (e.g., water damage and a theft) could face a much larger premium increase, potentially 20% or more, as the insurer views the property as a higher risk.
- Example 3: Conversely, maintaining a clean claims history for several years can lead to significant discounts, demonstrating responsible homeownership and reduced risk to the insurer.
Government Regulations and Their Effects
Provincial governments in Canada play a crucial role in regulating the home insurance market. Their oversight ensures fair pricing practices and consumer protection within the industry. While the federal government sets some overarching standards, the specifics of home insurance regulation, including pricing, are largely determined at the provincial level.Provincial regulatory bodies, such as the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario (FSRA) or the British Columbia Financial Services Authority (BCFSA), oversee insurers’ operations, including their pricing models.
These bodies have the power to investigate complaints, review rate filings, and ensure compliance with provincial regulations. Their primary objective is to maintain a stable and competitive home insurance market that protects consumers while allowing insurers to operate profitably.
Provincial Regulatory Oversight of Home Insurance Pricing
Each province has its own regulatory framework for home insurance pricing. Insurers typically must submit proposed rate changes to the provincial regulator for approval. The regulator reviews these proposals to ensure they are justified based on factors such as claims costs, operating expenses, and the overall financial health of the insurer. The review process aims to prevent excessive price increases while ensuring insurers can adequately cover their risks.
For example, if an insurer wants to raise premiums significantly, they must provide a detailed rationale to the regulator, demonstrating that the increase is necessary to maintain solvency and cover increasing claims costs. The regulator may approve the increase, partially approve it, or reject it entirely, depending on their assessment.
Government Initiatives to Enhance Home Insurance Affordability
Several provincial governments have implemented initiatives aimed at improving the affordability of home insurance. These may include programs that offer grants or subsidies to homeowners to mitigate the costs of flood mitigation or wildfire protection measures. Some provinces also collaborate with insurers to develop innovative insurance products or risk-sharing programs that can reduce premiums for certain groups of homeowners.
For instance, some programs offer discounts to homeowners who make improvements to their properties that reduce the risk of damage from natural disasters. Another example might involve government-backed reinsurance programs to help insurers manage catastrophic losses from widespread events like floods, lessening the need to increase premiums across the board.
Impact of Natural Disasters on Insurance Premiums and Regulations
Natural disasters, such as floods and wildfires, significantly impact home insurance premiums and regulations. Increased frequency and severity of these events lead to higher claims costs for insurers, necessitating premium increases to maintain profitability and solvency. This can disproportionately affect homeowners in high-risk areas. In response, regulatory bodies may adjust their oversight to account for these increased risks.
This could involve stricter building codes in high-risk zones, requirements for insurers to incorporate climate change projections into their risk assessments, or the development of specialized insurance products tailored to specific disaster risks. For example, after a major wildfire, the regulator might review insurers’ rate filings more closely to ensure they are not exploiting the situation to raise premiums excessively.
Furthermore, government initiatives to mitigate disaster risks, such as improved infrastructure or community-based disaster preparedness programs, may also influence future premium levels.
Consumer Considerations and Choices
Choosing the right home insurance policy can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options and actively comparing quotes can save you significant money in the long run. This section will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the Canadian home insurance market effectively.
Making informed decisions about your home insurance requires careful consideration of various factors. Understanding your needs, comparing policies, and knowing how to file a claim are all crucial aspects of responsible homeownership.
Tips for Obtaining Competitive Home Insurance Quotes
Shopping around for home insurance is essential to securing the best possible rate. Taking a proactive approach and utilizing available resources can lead to substantial savings. The following tips can help you find the most competitive quotes.
- Use online comparison tools: Many websites allow you to input your details and compare quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously. This saves time and effort.
- Contact insurers directly: Don’t rely solely on online comparison sites. Contacting insurance companies directly can sometimes uncover better deals or specialized options.
- Bundle your insurance: Combining your home and auto insurance with the same provider often results in discounts.
- Review your coverage annually: Your needs may change over time. Regularly reviewing your policy ensures you have the right level of protection.
- Consider increasing your deductible: A higher deductible will usually result in lower premiums, but be sure you can comfortably afford the higher out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim.
- Maintain a good credit score: Insurers often consider credit history when determining premiums. A good credit score can lead to lower rates.
- Improve your home’s security: Installing security systems and taking other preventative measures can demonstrate to insurers that your property is less risky, potentially lowering your premium.
Understanding Policy Details Before Purchasing
Before committing to a home insurance policy, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand its terms and conditions. Failing to do so could lead to unexpected costs or insufficient coverage in the event of a claim.
Carefully review the policy document, paying close attention to the following:
- Coverage limits: Understand the maximum amount the insurer will pay for different types of claims (e.g., fire damage, theft).
- Exclusions: Note what events or damages are not covered by the policy.
- Deductibles: Know how much you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in.
- Premium payment options: Understand the payment schedule and available methods.
- Cancellation policy: Familiarize yourself with the terms and conditions for cancelling the policy.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Home Insurance Coverages
Various types of home insurance coverage exist, each offering different levels of protection. Choosing the right coverage depends on individual needs and circumstances. Here are some common types and their associated considerations.
- Basic Coverage: This typically covers damage from fire, lightning, and other specified perils. It’s usually the most affordable option but offers limited protection.
- Broad Coverage: This expands on basic coverage to include additional perils such as wind, hail, and water damage (excluding flooding). It offers a good balance between cost and coverage.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This provides the most extensive protection, covering a wider range of perils, including things like sewer backups and vandalism. It’s the most expensive option but offers peace of mind.
- Additional Coverage Options: Consider adding optional coverages such as earthquake insurance, sewer backup insurance, or identity theft protection, depending on your specific risks and location.
Filing a Claim Effectively
Knowing how to file a claim efficiently and effectively can significantly impact the speed and success of your claim process. Following these steps will increase your chances of a smooth resolution.
- Report the incident promptly: Contact your insurer as soon as possible after the incident occurs.
- Document the damage: Take photos and videos of the damage to your property. Keep records of any related expenses.
- Cooperate with the adjuster: Provide all necessary information and documentation requested by the insurance adjuster.
- Understand the claims process: Familiarize yourself with your insurer’s claims procedures to avoid delays.
- Keep records: Maintain copies of all correspondence, documentation, and receipts related to the claim.
Illustrative Examples

Source: milesopedia.com
Understanding how home insurance premiums are calculated can be complex. Let’s illustrate this with a hypothetical scenario and a comparison of high- and low-risk properties. These examples are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered definitive premium calculations. Actual premiums vary widely based on many factors.
Toronto Family Home Insurance Premium Calculation
Let’s consider the Smiths, a family of four living in a detached, two-story home in Toronto. Their home is 2,500 square feet, built in 1985, and located in a relatively safe neighborhood. They have a mortgage of $800, They choose a comprehensive policy with a $2,000 deductible. Several factors influence their premium:
Home Value: $1,000,000 (This is the replacement cost of the house, not the market value).
Location: Toronto (Higher premiums due to higher property values and potential for claims).
Home Age and Construction: 1985 construction (Older homes might have higher premiums due to potential for wear and tear).
Coverage Level: Comprehensive (Higher premium than basic coverage).
Deductible: $2,000 (A higher deductible lowers the premium).
Security Features: Smoke detectors, burglar alarm (These features can result in a discount).
Claims History: No previous claims (A clean claims history leads to lower premiums).
Based on these factors, a reasonable estimate for the Smiths’ annual premium might be between $2,500 and $3,500. This is a broad range, as the precise premium depends on the specific insurer and their underwriting practices.
High-Risk vs. Low-Risk Home Premium Comparison
This visual comparison illustrates the premium differences between a high-risk and a low-risk home.
High-Risk Home: Imagine a waterfront property in a flood-prone area of Vancouver, built in 1920, with a history of water damage claims. The house is a large, older Victorian-style home requiring significant maintenance. It lacks modern security features. Its estimated value is $2,000,000. The annual premium could easily exceed $10,000, potentially much higher depending on the specific risks and the insurer’s assessment.
Low-Risk Home: Now consider a newly built, energy-efficient home in a quiet, suburban neighborhood in Calgary. The home is equipped with modern security systems, including a monitored alarm and fire suppression system. It’s a smaller, well-maintained bungalow with an estimated value of $700,000. The annual premium might be as low as $1,200 to $1,800.
Visual Representation:
Imagine two bars. The bar representing the high-risk home is significantly taller than the bar representing the low-risk home, visually demonstrating the substantial difference in premium costs. The taller bar for the high-risk home would be labeled with a premium amount significantly higher than the shorter bar for the low-risk home, reinforcing the visual representation of the cost difference.
The labels would also clearly indicate the key characteristics of each home, such as age, location, and security features, to further illustrate the factors influencing the premium difference.
Closing Notes: Home Insurance Premiums In Canada
Securing affordable and appropriate home insurance in Canada requires careful consideration of numerous variables. From understanding the risk factors associated with your property and location to comparing quotes from different insurers and leveraging available discounts, proactive planning is key. By being informed about the intricacies of home insurance pricing and the practices of insurance companies, you can effectively protect your investment and secure the best possible coverage for your needs.
Remember to regularly review your policy and adjust coverage as your circumstances change.
Q&A
What is the average home insurance premium in Canada?
There’s no single average, as premiums vary widely based on location, property type, and coverage. It’s best to get personalized quotes.
How often can I expect my premiums to change?
Premiums are typically reviewed annually. Changes can reflect factors like claims history, changes to your property, or shifts in the insurance market.
Can I pay my premiums monthly?
Most insurers offer monthly payment plans, though you might pay a slightly higher overall cost due to interest or fees.
What happens if I move to a different province?
You’ll need to notify your insurer of your change of address. Your premium may change depending on the risk profile of your new location.
What types of coverage are essential?
Essential coverage usually includes liability protection, coverage for damage to your home, and personal belongings. Consider additional coverage for specific risks like flooding or earthquakes based on your location.