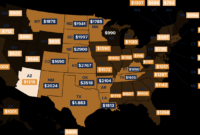
Home insurance premiums in the USA vary wildly, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for securing affordable and adequate coverage. From geographic location and property characteristics to your credit score and claims history, numerous elements contribute to the final premium. This guide will unravel the intricacies of home insurance costs, empowering you to make informed decisions.
This exploration will cover key aspects influencing your premium, including the role of location (high-risk vs. low-risk areas), the impact of your home’s features (age, size, materials), and the importance of your credit score and claims history. We’ll also delve into the different types of coverage available, optional add-ons, and strategies for finding affordable insurance, such as bundling policies and increasing your deductible.
Finally, we’ll examine the regulatory landscape and the influence of insurance companies in setting premiums.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Premiums: Home Insurance Premiums In The USA
Source: quote.com
Home insurance premiums in the USA vary significantly, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors can help homeowners make informed decisions and potentially save money on their insurance costs. This section will delve into the key elements that insurance companies consider when calculating premiums.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Costs
Your home’s location is a major determinant of your insurance premium. Areas prone to natural disasters like hurricanes, wildfires, earthquakes, or floods command higher premiums due to increased risk. Conversely, areas with lower risk profiles generally enjoy lower premiums. For example, coastal regions in Florida or states along the Gulf Coast typically face higher premiums because of hurricane risk, while areas in the Midwest with lower risks of severe weather might see lower premiums.
Similarly, homes located in areas with high crime rates may also see higher premiums due to increased risk of theft or vandalism. Conversely, a quiet, low-crime suburban neighborhood would typically result in lower premiums.
Home Features and Premium Calculations
The characteristics of your home itself significantly impact your insurance costs. Older homes, for example, may require more extensive repairs and renovations than newer ones, leading to higher premiums. The size of the home also matters, with larger homes generally costing more to insure. Finally, the construction materials used in building the house play a crucial role; homes built with fire-resistant materials may receive lower premiums than those constructed with more flammable materials.
| Feature | Impact on Premium | Example High-Cost Feature | Example Low-Cost Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of Home | Older homes generally have higher premiums due to increased risk of needing repairs. | A 100-year-old Victorian home requiring significant maintenance. | A newly constructed home with modern building codes. |
| Home Size (Square Footage) | Larger homes typically have higher premiums due to increased replacement costs. | A 5,000 square foot mansion. | A 1,000 square foot bungalow. |
| Construction Materials | Fire-resistant materials lower premiums; flammable materials increase them. | A home built with wood siding. | A home built with brick or stone. |
Credit Score’s Influence on Premium Rates
Your credit score is a significant factor in determining your home insurance premium. Insurance companies often view a good credit score as an indicator of responsible financial behavior, correlating it with a lower likelihood of filing claims. Therefore, individuals with higher credit scores often qualify for lower premiums. Conversely, those with poor credit scores may face significantly higher premiums.
A general guideline (this can vary by insurer): A credit score above 750 might result in the lowest premiums, while a score below 600 could lead to significantly higher premiums, potentially even resulting in denial of coverage.
Claims History and Future Premiums
Your claims history has a substantial impact on future premiums. Filing multiple claims, even for minor incidents, can lead to a significant increase in your premiums. Insurance companies view frequent claims as an indicator of higher risk, justifying the increase in cost. Conversely, maintaining a clean claims history, with no claims filed over several years, can result in lower premiums or even discounts.
Scenario: A homeowner with a clean claims history for five years might receive a lower premium compared to a homeowner who filed two claims in the past two years, even if the claims were for relatively minor incidents. The latter homeowner’s premiums could increase substantially.
Types of Home Insurance Coverage and Their Costs
Understanding the different types of home insurance coverage and their associated costs is crucial for securing adequate protection for your property and belongings. The cost of your policy will depend on several factors, including your location, the value of your home, and the coverage you choose. This section breaks down the key components and helps you understand what you’re paying for.
Home insurance policies typically bundle several types of coverage. The cost of each component varies significantly depending on your specific circumstances and the insurer. A higher coverage amount generally means higher premiums, but it also provides greater financial protection in case of a loss.
Coverage Types and Their Relative Costs
The primary components of a standard homeowners insurance policy are dwelling coverage, liability coverage, and personal property coverage. The cost of each varies greatly depending on factors like location, home value, and the level of coverage selected.
- Dwelling Coverage: This protects the physical structure of your home (walls, roof, foundation, etc.). It’s usually the most expensive component of your policy, representing a significant portion of the overall premium. The cost is directly tied to the replacement cost of your home, meaning a more expensive or larger home will command higher premiums.
- Liability Coverage: This covers legal costs and damages if someone is injured on your property or you’re held liable for damage to someone else’s property. Liability coverage is generally less expensive than dwelling coverage but is crucial for protecting your assets from potential lawsuits. Higher liability limits mean higher premiums, but provide greater financial protection.
- Personal Property Coverage: This protects your belongings inside your home, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing. The cost is typically lower than dwelling coverage but higher than liability coverage, and is often calculated as a percentage of your dwelling coverage. The cost increases with the value of your possessions and can be affected by factors like the presence of high-value items (jewelry, artwork).
Common Optional Coverage Add-ons and Their Costs
Many homeowners opt for additional coverage beyond the standard policy. These add-ons provide broader protection but increase the overall premium. The cost of these add-ons varies greatly depending on the specific coverage and your risk profile.
- Scheduled Personal Property: This provides more comprehensive coverage for high-value items like jewelry or antiques, often with agreed-upon values. The cost depends on the value and type of items scheduled. For example, insuring a $10,000 antique clock would significantly increase your premium compared to not insuring it.
- Identity Theft Protection: This covers expenses related to identity theft recovery. Costs vary depending on the extent of coverage offered. A basic plan might cost a few dollars per month, while more comprehensive plans could be significantly more expensive.
- Water Backup and Sewer Coverage: This covers damage from sewer backups or water that backs up from drains or sump pumps. The cost depends on factors like the age and condition of your plumbing system and the risk of flooding in your area. Homes in flood-prone areas will pay more.
Flood Insurance Cost Determinants and Hypothetical Example, Home insurance premiums in the USA
Flood insurance premiums are determined by several factors, including your home’s location within a flood zone, the value of your home, and the level of coverage you choose. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) maps flood zones, and properties in higher-risk zones will pay significantly more.
Hypothetical Example: A home in a high-risk flood zone with a replacement value of $300,000 might pay $2,000-$3,000 annually for flood insurance, while a similar home in a low-risk zone might pay only $500-$1,000 per year. These figures are illustrative and actual costs will vary.
Earthquake Insurance Cost Determinants and Hypothetical Example
Earthquake insurance premiums are influenced by factors like your home’s location in a seismically active area, the construction type of your home, and the level of coverage chosen. Homes built on unstable ground or with older construction methods will typically have higher premiums.
Hypothetical Example: A home in California built on a hillside with a replacement value of $500,000 might pay $2,000-$4,000 annually for earthquake insurance, while a similar home in a less seismically active area might pay only $500-$1,000. These figures are estimates and actual costs vary greatly depending on the specific location and risk factors.
Deductibles and Their Impact on Home Insurance Costs
Your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible will lower your annual premium, but you’ll pay more if you file a claim. Conversely, a lower deductible will result in a higher premium but lower out-of-pocket costs in the event of a claim.
Example: Let’s say a homeowner has two options: a $500 deductible with an annual premium of $1,500, or a $2,500 deductible with an annual premium of $1,200. The higher deductible saves $300 annually in premiums. However, if a $10,000 claim is filed, the homeowner with the $500 deductible pays $500 out-of-pocket, while the homeowner with the $2,500 deductible pays $2,500.
Finding Affordable Home Insurance
Finding the right home insurance policy shouldn’t break the bank. With a little research and smart strategies, you can secure comprehensive coverage without overspending. This section Artikels practical steps to compare quotes, leverage savings opportunities, and understand how various factors influence your premium.
Comparing Home Insurance Quotes
Effectively comparing home insurance quotes requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to ensure you’re getting the best possible deal.
- Gather Information: Before contacting insurers, compile essential information about your home, including its square footage, age, construction materials, and any security features. Also, note any claims you’ve filed in the past.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Several websites allow you to enter your information and receive quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously. This saves time and effort.
- Contact Insurers Directly: While online tools are helpful, contacting insurers directly can provide a more personalized experience and allow you to ask specific questions.
- Compare Coverage Details: Don’t just focus on price; carefully compare the coverage offered by each insurer. Ensure the policy meets your specific needs and adequately protects your assets.
- Read the Fine Print: Before committing to a policy, thoroughly review the policy documents to understand the terms, conditions, exclusions, and any limitations.
Bundling Home and Auto Insurance
Bundling your home and auto insurance with the same provider often results in significant savings. Insurers reward loyalty and efficiency by offering discounts for combining policies.For example, let’s say your annual home insurance premium is $1200 and your auto insurance premium is $800. Separately, you’d pay $2000. However, bundling might reduce your total cost to $1700, representing a $300 annual saving (15%).
This saving can accumulate over the years, making bundling a worthwhile strategy.
Impact of Deductible on Premium
Increasing your deductible, the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in, typically lowers your premium. This is because you’re accepting more financial responsibility in the event of a claim. However, choose a deductible you can comfortably afford.
| Deductible | Estimated Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| $500 | $1500 |
| $1000 | $1400 |
| $2000 | $1250 |
*Note: These are illustrative examples; actual premiums will vary based on several factors.*
Potential Insurance Discounts
Insurance companies offer various discounts to incentivize safe practices and responsible homeownership.
- Security System Discount: Installing a monitored security system, including burglar alarms and fire alarms, can significantly reduce your premium. The discount percentage varies depending on the insurer and the system’s features.
- Claim-Free Discount: Maintaining a clean claims history demonstrates responsible risk management and often leads to lower premiums.
- Home Improvement Discounts: Upgrades such as replacing your roof with fire-resistant materials or installing impact-resistant windows can lower your premiums.
- Multi-Policy Discount (Bundling): As discussed earlier, bundling home and auto insurance usually results in a substantial discount.
- Loyalty Discount: Some insurers reward long-term customers with reduced premiums.
- Senior Citizen Discount: Insurers sometimes offer discounts to senior citizens, reflecting their generally lower risk profile.
The Role of Insurance Companies and Regulations
Home insurance in the USA is a complex system shaped by both the actions of individual insurance companies and the regulatory frameworks set by state governments. Understanding this interplay is crucial for homeowners seeking affordable and adequate coverage.State Regulations and Minimum Coverage RequirementsState governments play a significant role in regulating the home insurance market. Each state establishes its own set of rules and regulations, impacting minimum coverage requirements and, indirectly, premium pricing.
These regulations are designed to protect consumers and ensure the solvency of insurance companies. For example, some states mandate minimum coverage amounts for dwelling coverage, liability, and personal property. Others might have specific requirements regarding hurricane or earthquake coverage in high-risk areas. Florida, for instance, has strict regulations regarding windstorm insurance, often resulting in higher premiums compared to states with less exposure to hurricanes.
California’s regulations reflect the state’s high wildfire risk, leading to specific requirements and potential surcharges for properties located in high-risk zones. These state-level differences highlight the importance of researching specific state regulations when comparing insurance policies.
Insurance Company Risk Assessment and Premium Determination
Insurance companies use sophisticated rating systems to assess the risk associated with insuring a particular property and then set premiums accordingly. These systems consider numerous factors, including the property’s location, age, construction materials, security features, and the homeowner’s claims history. A home located in a high-crime area with an older roof and outdated electrical system will generally receive a higher risk assessment than a newer home in a safe neighborhood with updated safety features.
Companies utilize statistical models and historical data to predict the likelihood of claims and their potential costs. This process involves analyzing vast amounts of data to identify trends and patterns that help them accurately price policies. The resulting premium reflects the estimated cost of potential claims plus the company’s operating expenses and profit margin.
Impact of Natural Disasters and Climate Change
The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, exacerbated by climate change, are significantly impacting home insurance premiums. Insurance companies are forced to reassess their risk models as they face escalating costs associated with claims related to wildfires, hurricanes, floods, and other extreme weather events. Areas prone to these events are seeing premium increases, sometimes dramatically. For example, coastal communities experiencing increased hurricane activity might face significantly higher premiums, while regions with elevated wildfire risk see similar increases.
Some insurers are even refusing to renew policies in high-risk areas, leaving homeowners with limited options and potentially forcing them to pay substantially higher premiums with other providers or go without coverage altogether. This leads to a situation where those most vulnerable are left with fewer options for protection.
Home Insurance Claim Process
Imagine a flowchart: The process begins with the homeowner filing a claim with their insurance company. This involves providing detailed information about the damage and supporting documentation like photos or videos. The insurance company then assigns an adjuster to investigate the claim. The adjuster inspects the damage, estimates the repair costs, and determines the amount the company will pay based on the policy’s coverage and deductibles.
If the claim is approved, the company issues a payment to the homeowner or directly to the contractor performing the repairs. Disputes can arise during this process, potentially leading to negotiations or even litigation if the homeowner and insurance company cannot reach an agreement. Once the claim is settled and the repairs are completed, the process is concluded.
This process, while seemingly straightforward, can be lengthy and complex, often requiring significant communication and documentation between the homeowner and the insurance company.
Last Point
Navigating the world of home insurance premiums in the USA can feel overwhelming, but understanding the key factors and available strategies empowers you to secure the best coverage at a price that fits your budget. By carefully considering your location, property features, credit score, and claims history, and by actively comparing quotes and exploring available discounts, you can significantly impact your premium.
Remember, proactive planning and informed decision-making are your best allies in securing affordable and comprehensive home insurance.
FAQ Guide
What is the average home insurance premium in the USA?
There’s no single average; premiums vary greatly based on location, coverage, and individual risk factors. Expect a wide range depending on these variables.
Can I get home insurance if I have a poor credit score?
Yes, but a lower credit score will likely result in higher premiums. Some insurers specialize in insuring individuals with less-than-perfect credit.
How often are home insurance premiums reviewed?
Premiums are typically reviewed annually. Your insurer may adjust your rate based on changes in your risk profile or market conditions.
What happens if I file a claim and then want to switch insurers?
Filing a claim will likely affect your premiums with your current and future insurers. Be prepared to disclose your claims history when applying for new coverage.
Is flood insurance included in standard home insurance policies?
No, flood insurance is typically purchased separately through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) or private insurers.